Cybersecurity
In an era of increasing reliance on digital systems and cloud services, Cybersecurity has become a top priority for organizations of all sizes and sectors. Cyber threats vary and evolve continuously, including malware, Ransomware attacks, Phishing, and targeted breaches of critical infrastructure. These attacks can lead to severe consequences, such as the leakage of sensitive data, prolonged service disruptions, and substantial financial losses.
The Cybersecurity Triad (CIA Triad)
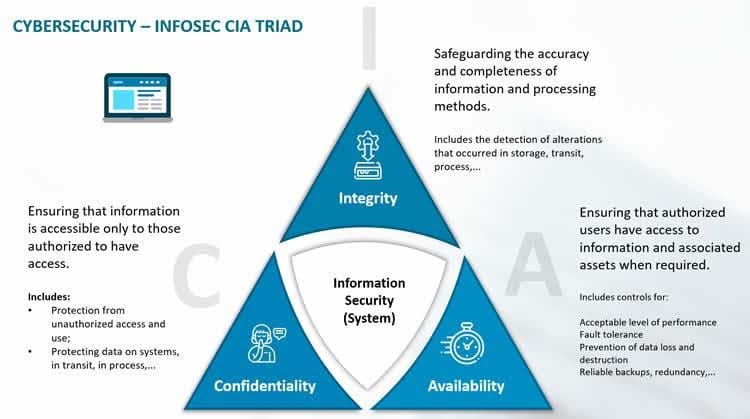
Cybersecurity is based on an essential triad known as the CIA model, which consists of: 1. Confidentiality: Protecting information from unauthorized access or disclosure. 2. Integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of data and preventing unauthorized modifications. 3. Availability: Ensuring the readiness of systems and data for authorized users when needed.
To achieve these pillars, a set of technical and administrative controls is applied. Technical controls include the use of Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), strong encryption, and Identity and Access Management (IAM).
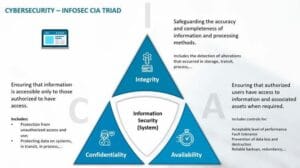
Infographic illustrates the trilogy of confidentiality, safety and availability
Administrative Controls and Incident Response
Cybersecurity is not limited to the technical aspect; it also includes administrative controls such as establishing a comprehensive information security policy and defining clear roles and responsibilities. Regular employee awareness is of utmost importance to reduce risks resulting from human errors, which are often the main entry point for attackers.
Incident Response operations form a major part of the security strategy, where there must be clear plans for reporting, analysis, containment, and recovery from attacks. Cybersecurity programs also integrate with business continuity and disaster recovery to ensure the rapid restoration of sensitive systems and services after any breach.

Image of a security monitor in a cybersecurity operations center (SOC)
Challenges and Modern Trends
Some critical sectors require compliance with strict regulatory standards, such as national frameworks or sector-specific requirements for banks and energy. Periodic penetration assessments and security tests help uncover vulnerabilities before they are exploited by attackers. With the spread of cloud services and remote work, the importance of identity and access management and endpoint security has emerged. There has also been an increased reliance on Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions for monitoring logs and detecting unusual activities. In the end, cybersecurity is an ongoing journey that requires constant updates to controls and skills to keep pace with the rapid evolution of threats.