Corporate Governance
Corporate Governance is considered the regulatory framework through which operations within the organization are managed. It is a set of rules and practices that ensure transparency, accountability, fairness, and the protection of the rights of all stakeholders. The primary goal of governance is to achieve a precise balance between the interests of owners, executive management, employees, customers, and society as a whole. When governance is strong and effective, it significantly reduces the risks of corruption and mismanagement, and increases the confidence of investors and partners in the organization’s sustainability.
Essential Pillars of Governance
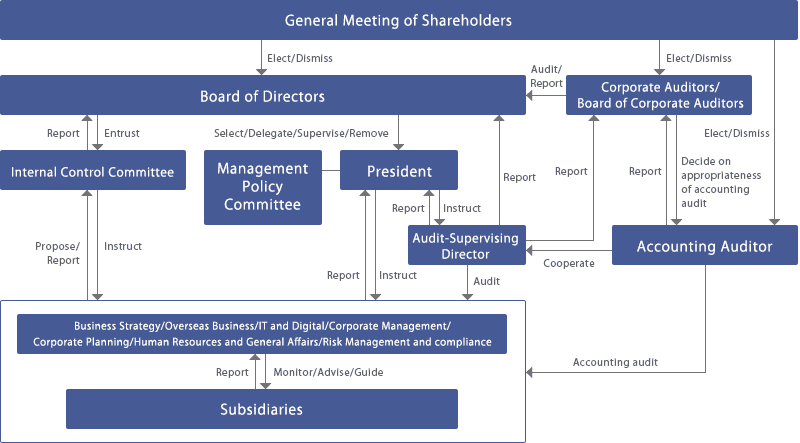
Effective governance begins with the formation of a board of directors that possesses independence, efficiency, and the necessary expertise to set the overall strategy and monitor the performance of executive management. The presence of specialized committees affiliated with the board, such as the audit committee, risk committee, and compensation committee, helps deepen oversight and distribute tasks in a balanced and professional manner. The roles and responsibilities of each committee, as well as the boundaries separating them from executive management, are clarified through approved internal charters (Charters).
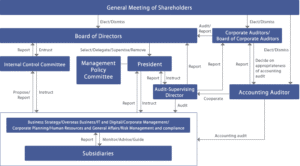
A diagram showing the relationship between the board, committees, and executive management
Written policies and procedures form the backbone of governance, as they define the rules for decision-making, delegation authorities, and mechanisms for interaction with internal and external parties. Prominent examples of these policies include: conflict of interest policy, disclosure and transparency policy, and risk management policy. Adhering to these policies helps unify practices and reduce individual interpretations, thereby enhancing justice and equality among employees and stakeholders.
Oversight, Accountability, and Sustainability
Internal controls and internal audit are considered an essential part of the governance system, as they evaluate the effectiveness of operations and internal controls, identify gaps, and opportunities for improvement. Independent external audit also contributes to enhancing the credibility of financial reports before regulatory bodies and investors. To ensure accountability, channels for reporting violations (Whistleblowing) and protecting whistleblowers are a vital element for early detection of improper behaviors.
Corporate governance increasingly supports the concept of sustainability by integrating environmental and social aspects with governance in a single framework known as (ESG). This approach aligns with the requirements of global financial markets and the increasing expectations from society regarding the role of companies in sustainable development. In conclusion, governance is not limited to mere compliance with regulations, but it is a culture and daily behavior that reflects values of integrity and responsibility within the organization.
Governance values infographic: Transparency, Accountability, Justice, Sustainability